With the accelerated development of new power systems, distribution transformers are undergoing a profound transformation from conventional equipment to intelligent devices. This article systematically examines the driving factors, key technologies, implementation pathways, and future trends of this intelligent transformation, providing valuable insights for industry upgrading.
1. Three Major Drivers of Intelligent Transformation
1.1 Grid Development Requirements
- Rising penetration of distributed energy resources (projected to reach 40% by 2025) necessitates bidirectional power flow management
- Increased power electronic devices leading to severe harmonic pollution (300% growth in scenarios with THD>8%)
- Growing demand for power supply reliability (urban target: 99.99%)
1.2 Technological Advancements
- Sensing technology: Miniaturized CT/PT units (accuracy up to 0.2S class)
- Communication technology: HPLC+RF dual-mode communication (latency <100ms)
- Algorithm technology: Deep learning-based fault diagnosis (accuracy >95%)
1.3 Policy and Standard Guidance
- NDRC’s “Distribution Network Intelligent Transformation Guidelines” outlining implementation timelines
- IEC 61850-7-420 standard ensuring device interoperability
- Carbon trading mechanisms promoting digital energy efficiency management
2. Core Intelligent Technology Framework
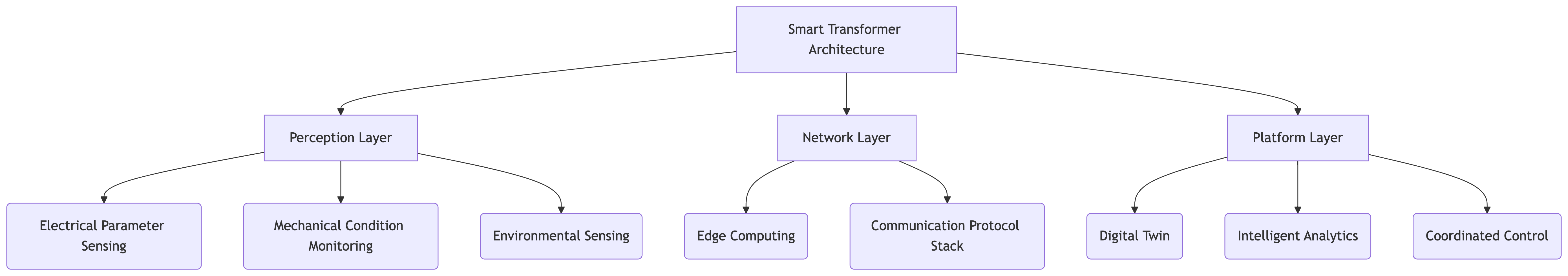
3. Practical Application Scenarios
3.1 Adaptive Voltage Regulation
- Guangdong pilot project achieving ±5% automatic voltage adjustment
- Load fluctuation response time reduced to 30 seconds
3.2 Predictive Maintenance
- Shandong case study: Combined dissolved gas analysis and vibration monitoring
- Fault prediction accuracy improved to 92%
3.3 Demand Response
- Jiangsu virtual power plant project
- 200 smart transformers aggregated for peak shaving
4. Recommended Implementation Pathways
4.1 Technology Roadmap
| Phase | Timeline | Key Tasks |
|---|---|---|
| Pilot Stage | 2023-2025 | Core equipment智能化transformation |
| Promotion | 2025-2028 | Feeder-level coordinated control |
| Maturity | 2028-2030 | Fully autonomous operation |
4.2 Economic Benefit Analysis
- Initial investment increase: 15-20%
- O&M cost reduction: 35%
- Asset utilization improvement: 25%
5. Future Development Trends
5.1 Technology Convergence
- Integration of superconducting materials with intelligent control
- Blockchain applications in asset trading
5.2 Standard System Improvement
- Industry-wide data interface standardization
- Intelligent maintenance protocol development
5.3 Business Model Innovation
- Device-as-a-Service (DaaS) model adoption
- Integration of carbon asset management with intelligent maintenance
Conclusion
The intelligent transformation of distribution transformers represents a critical component in building new power systems, requiring coordinated efforts across the industry chain. We recommend focusing on breakthroughs in smart sensing and edge computing technologies while strengthening standard system development and cultivating professional maintenance service markets. Ultimately, this will enable distribution equipment to achieve a qualitative leap from “passive maintenance” to “active service.”

